Genetic Testing
In our genetic diagnostics laboratory, we perform molecular genetic, molecular cytogenetic and cytogenetic testing, using state-of-the-art high-throughput (next-generation) sequencing technology in disease-specific gene panels along with MLPA analysis, array CGH and conventional karyotyping.
Our services are offered in collaboration with “Medizinisches Versorgungszentrum der UMG Bereich Humangenetik“. All analytical and processing steps in our diagnostic lab are performed under controlled and monitored conditions. We have received accreditation by the German Accreditation Body (DAkkS) in accordance with DIN EN ISO 15189:2014 within the scope of “Medical Laboratory Services” for the areas of “Molecular Human Genetics” and “Cytogenetics”.
We are dedicated to use the latest findings made by our researchers in their various activities to directly support, improve and further develop our routine diagnostic services. This allows us to continually expand our range of tests and to offer genetic diagnostics on the highest technical level and reflecting the latest scientific knowledge.


Molecular Genetics
The goal of molecular genetic testing is to either confirm or exclude the genetic change that causes a specific condition of interest.
With next-generation sequencing (NGS) technology, we have powerful tools to offer comprehensive analysis at reasonable prices.
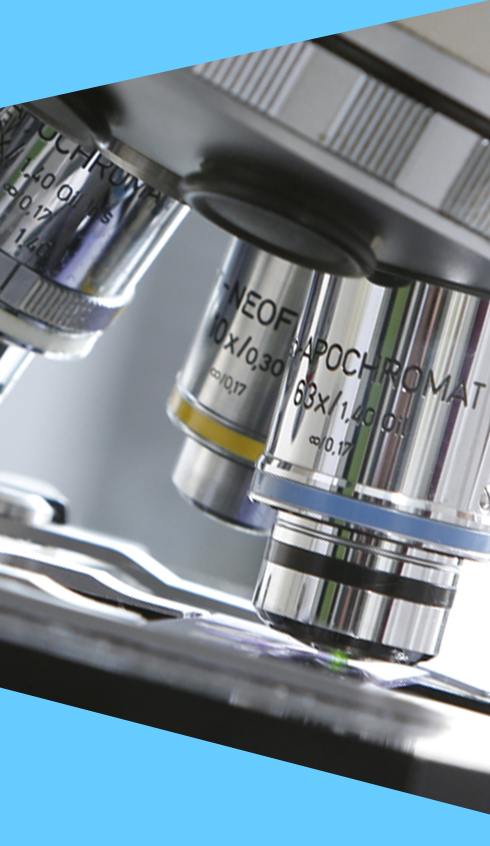
Cytogenetics
In classical cytogenetic diagnostics, we investigate chromosomes under the light microscope for changes that affect either their number (aneuploidies) or their structure (e.g. inversions, translocations, duplications or deletions).
This conventional method of chromosome analysis continues to be a useful tool for various indications and is applied for prenatal or postnatal diagnostics.



Molecular Cytogenetics
With high-resolution molecular cytogenetic methods, we can detect structural chromosomal changes that are too small to be visible with a light microscope in conventional karyotyping.
We use array CGH (array-based comparative genomic hybridization) analysis to search at the whole-genome level for submicroscopic chromosome aberrations such as microdeletions or duplications.

